Association of Cardiovascular Disease Management Drugs with Lewy Body Dementia
By Sonja Scholz, M.D., Ph.D.
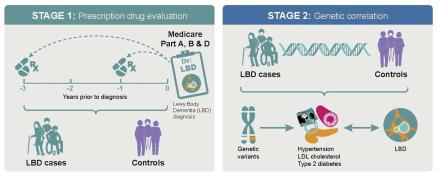
Lewy body dementia (LBD) is a complex brain disease that presents with visual hallucinations, changes in attention, slowed movements, sleep problems, and other disabling symptoms. Therapies that slow down, halt, or delay the disease onset currently do not exist. To address this problem, Dr. Sonja Scholz from NINDS and Dr. Ruth Pfeiffer from the National Cancer Institute (NCI), performed an epidemiological analysis of LBD patients and controls. They reviewed data from the Medicare database to identify drugs that may lower the risk of developing the disease.
They found that LBD patients treated with medications for cardiovascular disease (e.g., high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, or high lipids) had a lower risk of developing dementia. Their findings were supported by evaluating the genomes of patients with LBD, which demonstrated overlaps in the genetic risk profile of LBD and cardiovascular diseases. The study suggests that strict management of elevated blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, and high lipids may benefit this patient population.
New Direct Links Discovered Between the Brain and its Surrounding Environment
By NINDS Staff
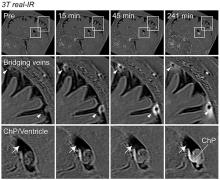
In collaboration with researchers from Washington University in St. Louis, Dr. Daniel S. Reich, head of the Translational Neuroradiology Section, along with Postdoctoral Fellow Dr. Serhat V. Okar, Staff Clinician Dr. María Inés Gaitán, and Staff Scientist Dr. Govind Bhagavatheeshwaran Nair, conducted a landmark study examining the brain’s connections to the immune system. The results revealed direct connections between the brain and its tough protective covering – the dura mater – opening new avenues for exchange of fluids and cells.
The findings, supported by advanced MRI and microscopic imaging, suggest that arachnoid cuff exit (ACE) points may play a critical function in disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis, by affecting waste clearance and immune system interactions. Additionally, the researchers found that aging might increase the leakiness of these points, potentially affecting the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Click here to learn more.
Cerebral Microbleed Patterns and Cortical Amyloid-β: The ARIC-PET Study
By Tam Vo, Ph.D.
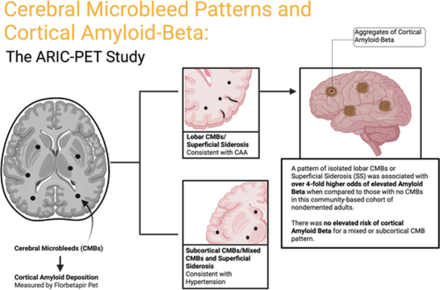
In this study, published in Stroke (also available in Stroke Podcast), Derrick Okine in Dr. Rebecca Gottesman's group and colleagues investigated the importance of cerebral microbleeds (CMBs), which contribute to hypertension and cognitive decline, beyond its association with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) using florbetapir positron emission tomography (PET). Specifically, the researchers focused on the correlation between CMB patterns and cerebral Aβ (amyloid-β) deposition in community-based, dementia-free adult participants.
They found no significant association between subcortical or mixed CMBs and Aβ positivity. However, a pattern of isolated lobar CMBs or superficial siderosis (SS) was associated with over 4-fold higher odds of elevated Aβ. The odds ratios were higher for lobar-only CMBs in four subgroups: women, Black participants, apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 noncarriers, and cognitively normal individuals. The finding could help physicians with patients who experienced CMBs but are not diagnosed with CAA. The study also highlights the need for further investigation into other contributing factors that have important roles in cognitive deficits.
Molecular Determinants for Cold Adaptation in an Antarctic Na+/K+-ATPase
By Miguel Holmgren, Ph.D., and Duilio Correa
Enzymes from ectotherms living in chronically cold environments have evolved structural innovations to overcome the effects of temperature on catalysis. In a recent study, Dr. Miguel Holmgren, Principal Investigator, Molecular Neurophysiology Section, and his team identified which genetic mutations to a transmembrane enzyme confer cold adaptability to the Antarctic octopus Pareledone sp – an animal that normally lives in frigid waters below 0 °C.
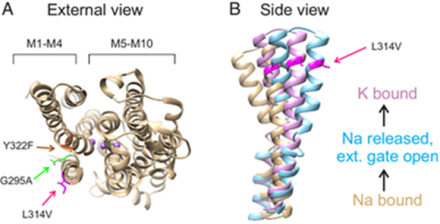
Dr. Holmgren’s team studied the ion pump Na+/K+-ATPase enzyme, which catalyzes the decomposition inside the cell of the chemical fuel known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to move Na+ and K+ across the cell membrane and plays a vital role in several cellular processes. Using the egg cells of an African clawed frog to produce Na+/K+-ATPases, they studied various chimeras between the Antarctic ion pump and a temperate ortholog from an octopus species that lives in waters of 14–20 °C.
Even though the ion pump has ~1030 amino acids, only 12 substitutions can turn a temperate ion pump into an Antarctic one. Remarkably, one leucine facing the protein/lipid interface is the crucial one in determining how well the ion pump works at low temperatures.
Layers of Inhibitory Networks Shape Receptive Field Properties of AII Amacrine Cells
By Tam Vo, Ph.D.
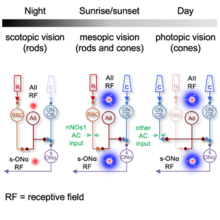
The rod and cone pathways in mammalian retina mediate visual signal under various light conditions. In a recent study, published in Cell Reports, Drs. Amurta Nath and William Grimes in Dr. Jeffrey Diamond’s group conducted to understand how AII (“A-two”) receptive fields (RF) in mouse retina are shaped in different light conditions via rode and cone pathways.
Through electrophysiology recording, they found that inhibitory surround, a component in RF organization to help transmit visual properties, exists in mesopic and photopic levels but not at the scotopic level. Even more fascinating is that ablating neuronal nitric oxide synthase type-1 (nNOS-1) ACs, an interneuron that provides neurotransmission, could interact, and remove AII surround inhibition under mesopic (dusk/dawn) conditions, but not photopic ones. These findings demonstrate how multiple layers of neural circuitry interact to encode signals across a broad physiological range, providing a glimpse into the complex and remarkable workings of the mammalian eye.
Multi-Modal Proteomic Characterization of Lysosomal Function and Proteostasis in Progranulin-Deficient Neurons
By Tam Vo, Ph.D.

Progranulin (PGRN) is a lysosomal glycoprotein associated in various neurodegenerative diseases. Mutations in the GRN genes found in inherited frontotemporal dementia (FTD) can reduce the expression of PGRN. In a recent study published in Molecular Neurodegeneration, Saadia Hasan, Michael Fernandopulle, and Stewart Humble in Dr. Michael E. Ward’s group co-led a project to understand the roles of PGRN and the effect of PGRN deficiency in lysosomal functions.
The researchers leveraged multifaceted proteomics techniques to characterize the dynamic lysosomal biology in living human neurons and fixed mouse brain tissues. Researchers found that subnormal PGRN concentration in mutated GRN influence multiple factors in lysosome such as increases lysosomal PH, amplifies v-ATPase subunits and, in turn, decreases lysosome degenerative activities. This creates a cascaded effect in the global proteostasis of neurons. These findings show that PGRN is a critical regulator of lysosome activities and provides an example for adapting new, improved proteomics methods to dissect neuronal lysosome biology.
By NINDS Staff
Norepinephrine is derived from dopamine, which is deficient in the brains of people with Parkinson’s disease. In a recent study, a team of researchers led by Dr. David S. Goldstein, Principal Investigator, Autonomic Medicine Section, NINDS, conducted positron emission tomography (PET) scans of the heart to gain a better understanding into levels of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine.
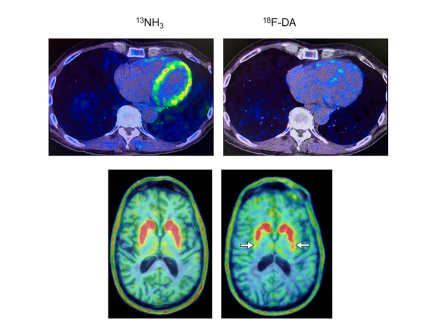
The researchers found that at-risk individuals with low 18F-dopamine-derived radioactivity in the heart were highly likely to develop Parkinson’s disease or Lewy body dementia during long-term follow-up, compared to individuals with the same risk factors but with normal radioactivity. The study supports the view that synuclein disorders affect the nerves of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates automatic body processes like heart rate and blood pressure.
To read more about this breakthrough study, please click here.
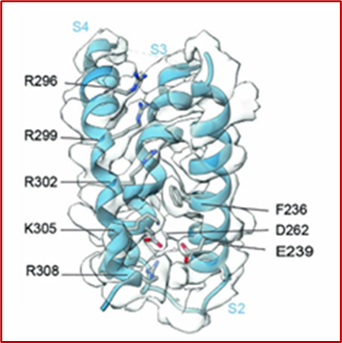
Inactivation of the Kv2.1 Channel Through Electromechanical Coupling
By Alynda Wood, Ph.D.
Contributions of the Sodium Leak Channel NALCN to Pacemaking of Medial Ventral Tegmental Area and Substantia Nigra Dopaminergic Neurons
By Alynda Wood, Ph.D.
The neurotransmitter dopamine plays a role in a wide range of behaviors, including psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia and movement disorders such as Parkinson’s Disease. Two of the major sources of dopamine in the brain are adjacent structures called the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA). SNc and VTA neurons fire action potentials in a consistent, rhythmic fashion generated by the cell’s internal mechanisms (rather than external input, such as that from other neurons), a phenomenon called “pacemaking.” This results in a steady release of dopamine, which is necessary for normal movements and reward behaviors.
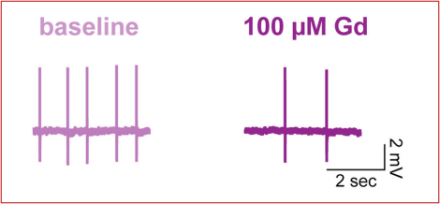
In a project lead by former graduate student Dr. Dana Lewis, NINDS Senior Investigator Dr. Zayd Khaliq tested the role of the sodium leak channel NALCN in maintaining pacemaker activity in both VTA and SNc dopamine neurons. First, they used a technique called in situ hybridization to identify NALCN RNA in dopaminergic neurons. They found that VTA had lower levels of NALCN RNA than SNc. Next, they used a technique called slice electrophysiology, which allows scientists to measure the electrical properties of neurons in a carefully-controlled setting. Their results demonstrated that NALCN was a key driver of pacemaking in the VTA. In contrast however, inhibiting NALCN in SNc had no effect on pacemaking, though it did increase the sensitivity of the cells to external inputs. Understanding the different mechanisms used for different populations of dopamine neurons could pave the way for new drugs that selectively target specific subpopulations of neurons.
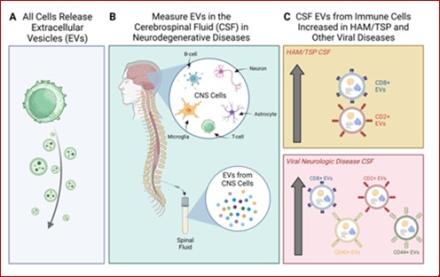
Viral Immune Signatures from Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicles and Particles in HAM and Other Chronic Neurological Diseases
By Michelle Pleet, Ph.D.
In the recent publication entitled “Viral Immune signatures from cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles and particles in HAM and other chronic neurological diseases” in Frontiers in Immunology, a team led by postdoctoral Fellow Michelle Pleet, Ph.D. and Senior Investigator Steven Jacobson, Ph.D., delves into the importance of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in neurological disease. EVs are tiny packets of information released from cells into the blood and other bodily fluids such as spinal fluid. In this paper, the authors investigated whether EVs obtained from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from healthy volunteers and patients with neurological disease triggered either by viruses or by other causes could be traced back to the cell types from which they originated by their surface markers, and thereby be used to understand the underlying mechanisms of disease.
In this work, the team observed that EVs from specific T-cell subtypes were upregulated in the CSF in diseases caused by viruses, as particularly exemplified in patients with HAM/TSP (human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1)-associated myelopathy / tropical spastic paraparesis), a chronic neurological disorder caused by a retrovirus. Results from the study may play an important role in identifying new biomarkers associated with chronic neurologic diseases in which viruses are known or suspected to play a role, thus leading to more targeted treatments and possible prevention strategies.
By Prashant Chittiboina, M.D.
Cushing’s disease results from an excess of the steroid hormone in humans, often caused by a small tumor in the pituitary gland. This tumor leads to an overproduction of the hormone ACTH, which in turn prompts the adrenal glands to release too much cortisol—a steroid hormone. Excessive cortisol can have devastating effects, including weight gain, brittle bones, and growth arrest.
While surgery to remove the tumor is the primary treatment, the disease can return if even a tiny portion of the tumor remains. One of the challenges clinicians face is determining if the treatment has been successful, given the natural fluctuation of ACTH and cortisol levels in the body throughout the day.
In a recent study, Dr. Prashant Chittiboina, the principal investigator, and his team led by first author, Dr. Reinier Alvarez, studied over 200 patients that were treated for Cushing’s disease at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, MD. They focused on ACTH and cortisol levels at specific times (midnight and morning). They discovered that ACTH levels in those with active Cushing’s disease fluctuated less than in healthy or successfully treated individuals. When the tumor was entirely removed, this fluctuation returned to normal. Essentially, if there's a high variation in ACTH levels, it indicates effective treatment. Moreover, the study found that untreated patients had a narrower, but higher, range of ACTH values throughout the day. A drop of 50% in ACTH levels was also seen as an indicator of successful treatment.
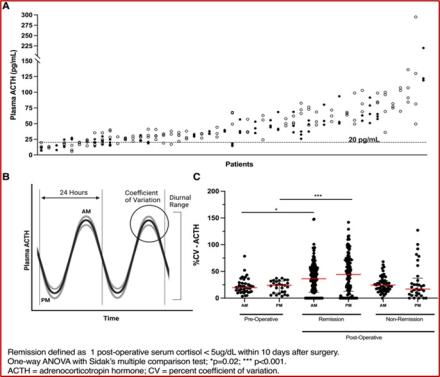
The key takeaway is that by observing the variability in ACTH levels, rather than just the absolute amounts, clinicians now have a more effective way to gauge treatment success. This approach offers a new avenue for designing clinical trials and assessing treatment outcomes more precisely.
Uncovering New Ion Pathways in the P2X Receptor
By Nina Lichtenberg, Ph.D.
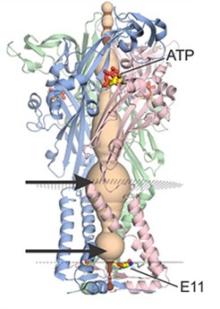
P2X receptors are ATP-activated cation channels found throughout the body, including in the nervous system. They play a range of important roles, including transmitting gustatory signals, mediating neuropathic pain, and regulating immune responses. Resolving the biophysical mechanisms of P2X receptor channels can inform the development of more efficient, targeted drug therapies.
Many studies have probed the mechanisms of P2X channels, but the precise function of lateral fenestrations, special pathways buried deep within these channels that can transport ions into binding sites, remains unknown. In a recent study, Dr. Kenton Swartz and his team used recently solved structures and whole-cell electrophysiology to take a closer look at these pathways in P2X receptors. They found that lateral fenestrations allow ions to enter and exit the internal pore at the intracellular end of the membrane and specific structural elements of the pathways, called cytoplasmic caps, help determine ion selectivity.
Additional research is needed to determine if these features are seen across P2X receptor subtypes. Future studies may also explore how ion selectivity of subtypes support various physiological functions in the nervous system, cardiac muscle, and beyond.
Monocyte-derived IL-6 Programs Microglia to Rebuild Damaged Brain Vasculature
By Alynda Wood, Ph.D.
Cerebrovascular injury (CVI) can occur after infections, injury, stroke, neurodegeneration, and autoimmune disease, resulting in damage to surrounding brain tissue. In a study published in Nature Immunology, Dr. Bo-Ran Choi, a Postdoctoral Fellow in the lab of Dr. Dorian McGavern, examined the role of repair-associated microglia (RAM) in recovery from CVI. RAMs are a subtype of microglia previously discovered by the McGavern lab, however, until now it was unclear how these cells acquired their ability to repair damaged brain vasculature.
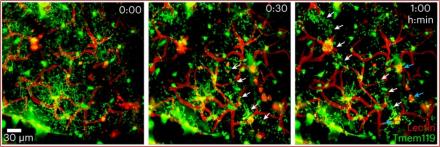
Using a mouse model, the researchers first established that CVI induces the generation of RAMs and that their numbers correlated with CVI severity. Next, they examined postmortem human brain tissue and identified RAMs present after stroke. Finally, they returned to mice and determined that infiltrating monocytes (a type of white blood cell) released a cytokine called interleukin-6 that “programmed” RAMs to repair blood vessels after CVI. These data provide a molecular and cellular basis for how monocytes instruct microglia to repair damaged brain vasculature and promote functional recovery after injury and suggest that future treatments aimed at increasing RAM numbers could help CVI patients in the clinic.
Cryo-EM Tomography and Automatic Segmentation Delineate Modular Structures in the Postsynaptic Density
By Nina Lichtenberg, Ph.D.
Under postsynaptic densities (PSDs) are large protein complexes that line postsynaptic membranes of excitatory neuronal synapses. PSDs are composed of more than 1000 proteins, including receptors, scaffold proteins, and signaling enzymes. Advances in super-resolution microscopy have recently led to a better understanding of PSD organization but many molecular substructures within these proteins remain uncharted due to technical limitations.
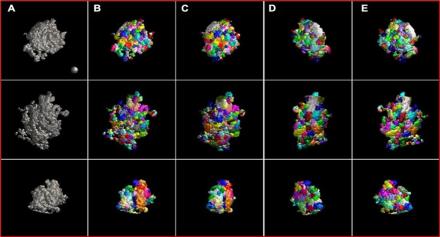
Using cryo-electron (cryo-EM) tomography on rat brain tissue, Dr. Thomas Reese and his team reconstructed PSDs in 3D and examined individual PSD substructures using a new, optimized automated segmentation approach. Data analysis revealed an array of modules that were mostly tens of nanometers in size. They also identified modules that span the entire thickness of the PSD, called trans-PSD modules. In addition to developing a more efficient segmentation method, this study adds to growing evidence that PSDs are composed of modules of various sizes and compositions, which may play a key role in synaptic function
In Vivo MRI is Sensitive to Remyelination in a Nonhuman Primate Model of MS
By Alynda Wood, Ph.D.
The NINDS intramural researchers took an important step forward in measuring a key feature of multiple sclerosis (MS), a debilitating disorder affecting millions. MS causes pathological changes to myelin, a protective coating that covers nerves, leading to neuron damage and dysfunction. The changes in myelination that occur in MS are dynamic; destruction of myelin (demyelination) can be followed by myelin repair (remyelination). Understanding remyelination mechanisms could be key to treating MS. However, studying remyelination has historically been very challenging because it is difficult to measure in people with MS.
To address this problem, Dr. Maxime Donadieu (a Postdoctoral Fellow), Dr. Nathanael Lee (then a graduate student), and Dr. Pascal Sati (a Staff Scientist), all in the lab of Dr. Daniel Reich, took critical steps to establish that high resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be effectively used to monitor demyelination and remyelination in a marmoset model of MS. Marmosets are an important translational model for MS because they capture key features of the disease not seen in rodent models. The study, published in eLife, shows that certain changes in the in vivo MRI signal accurately captured the remyelination observed in the postmortem brain tissue. They also tested whether corticosteroid treatment influenced remyelination, finding no effect. (However, the authors note that a different time course of treatment could show different results.) Overall, these results could provide a crucial foundation for the development of techniques that can be used in the clinic to measure remyelination in MS patients and open the door to test remyelinating therapies.
Researchers Identify Large Genetic Changes Related to Dementia Risk
By OSD Staff
In a collaborative study led by Sonja W. Scholz, M.D., Ph.D., a Lasker Clinical Research Scholar, researchers from NINDS and NIA discovered several structural variants that could be risk factors for Lewy body dementia (LBD) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD).
Unlike more commonly studied mutations, which often affect one or a few DNA building blocks called nucleotides, structural variants represent at least 50, but often hundreds, or even thousands, of nucleotides at once, making them more challenging to study. Furthermore, a previously unknown variant in the gene TPCN1 was found in samples from patients with LBD, a disease, that like Parkinson’s disease, is associated with abnormal deposits of the protein alpha-synuclein in the brain.
By combining cutting-edge computer algorithms capable of mapping structural variations across the whole genome with machine learning, the research team analyzed whole-genome data from thousands of patient samples and several thousand unaffected controls. Moreover, investigators looked at a group of 50 genes implicated in inherited neurodegenerative diseases and were able to identify additional rare structural variants and two well-established risk factors for FTD changes in the C9orf72 and MAPT genes.
“With each discovery, we shed light on the mechanisms behind neuronal cell death or dysfunction, paving the way for precision medicine to combat these debilitating and fatal disorders” (Dr. Bryan J. Traynor, Senior Investigator, NIA).
Advances in ALS: Unraveling Its Causes and Finding Treatments
By NIH News in Health Staff
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease) causes muscles to weaken over time and eventually leads to death. Most cases of ALS are sporadic; however, genetic causes account for 15% or less of ALS cases. The majority of gene mutations found in ALS lead to the dysfunction of a protein called TDP-43. Dr. Michael Ward, Senior Investigator, NINDS is studying the role of this protein in relation to ALS.
“The first genetic cause of ALS was discovered nearly 30 years ago, with a gene called SOD1…Now, there are over 50 different genes that the research community has identified that can independently cause familial forms of ALS. Leveraging advances in genomics and cellular disease models, we can now link some of these genes into unifying molecular pathways, for example our discovery that loss of TDP-43 function directly impacts the splicing of UNC13A, another ALS gene that plays a key role in synaptic biology” (Dr. Ward).
Dr. Ward’s lab is testing ways to measure when TDP-43 becomes dysfunctional in cells, but before it has done damage. This will allow them to see if treatments can prevent or slow the protein from doing damage. Click here to read more.
Progress in Understanding Acetylcholine's Role in Cognition and Disease
By Carlo Quintanilla, Ph.D.
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a chemical messenger with a variety of important functions in the nervous system. In the brain, ACh plays a crucial role in many cognitive functions, including attention, learning, and memory. In the peripheral nervous system, ACh is important for nerve muscle transmission. While the functions of cholinergic neurons have been extensively investigated and identified, recent studies have shown that a subset of cholinergic neurons, called basal forebrain cholinergic neurons (BFCNs) have a functional organization more varied than previously thought.
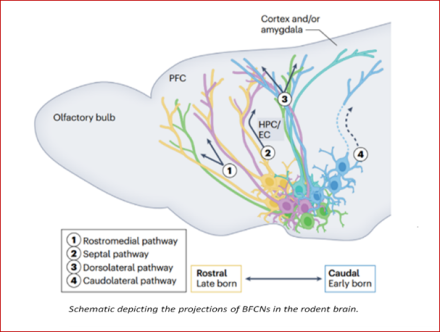
In this recent review, Dr. Lorna W. Role and her team, led by post-doctoral researcher Dr. Mala Ananth, summarize the current understanding of the developmental origins, connectivity, and function of BFCNs in rodents and how they give rise to cognition-related behaviors. Specifically, Ananth et al. brings to light the factors that contribute to the diversity of BFCNs and the signals they communicate in the brain. Ananth et al. also provides a roadmap of recent advances in experimental techniques, including transcriptomic and epigenomic profiling, imaging techniques, and compartment-specific measurements of cholinergic dynamics. Importantly, Ananth et al. propose how these advancements and tools may help address long-standing questions in the field, as well as support the development of new therapies for neurological disorders that affect cognition, such as Alzheimer's disease.
Link Between Low Education and Dementia may be Partially Explained by Vascular Risk Factors
By Nina Lichtenberg, Ph.D.
Lower education in childhood is associated with a greater risk of dementia later in life. Among other factors, this pattern may be explained by unequal access to health-promoting resources, which leads to poorer cardiovascular health. However, whether vascular risk factors in mid-life contribute to this disparity is unknown.
In a large study, Dr. Rebecca Gottesman and her collaborators assessed the relationship between educational attainment and dementia in a cohort of 13,368 Black and White adults. Participants were part of the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study, a long-running community-based study designed to better understand atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, and how risk factors vary by race, sex, and other demographics. Here, Dr. Gottesman’s team found that up to 25% of the link between education and dementia was explained by vascular risk factors in mid-life, including blood pressure, fasting blood glucose, body mass index, and smoking. Their analysis also showed that more education was associated with an 8-44% lower risk of dementia compared to grade-school level education. There was a much weaker relationship between education and dementia in those who developed dementia after stroke, a high-risk group. Overall, the results identify mid-life vascular risk factors as key mediators of the link between education and dementia and may inform new prevention strategies, potentially in early life.
While controlling these factors lowers dementia risk, this is unlikely to fully address large disparities, according to the authors. More research is needed to understand the multifaceted ways in which lower education leads to dementia.
Interictal Discharges in the Human Brain are Travelling Waves Arising from an Epileptogenic Source
By Alynda Wood, Ph.D.
The epilepsies refer to a collection of disorders that cause seizures (a burst of abnormal electrical activity in the brain) which can lead to involuntary movements, sensations, emotions, loss of consciousness, and other debilitating symptoms. In cases where epilepsy is unresponsive to medication, the best course of treatment is sometimes surgically removing the brain tissue where the seizures originate. The current gold standard for identifying the origin of epileptic activity in the brain is to visually inspect data recorded from electrodes directly on the surface of the brain (called intracranial electroencephalography, or iEEG) during seizures.
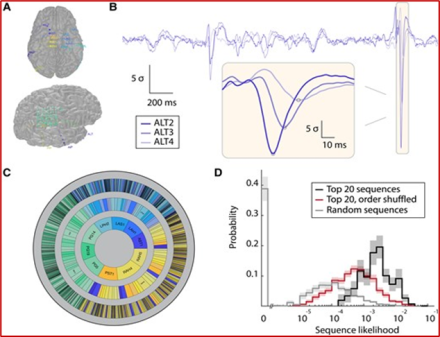
In a recent paper, Dr. Joshua Diamond, a Neurosurgery Resident working in the laboratory of Dr. Kareem A. Zaghloul, investigated whether waves of abnormal brain activity that occur between seizure episodes (called interictal discharges) could also be used to identify where the seizure originated. To do this, they used a novel computational approach. adapted from techniques used in sonar, radar, geophysics and acoustics, to more accurately pinpoint seizure origins based on how abnormal activity spreads through the brain. They analyzed iEEG data recorded from 40 patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy prior to undergoing surgery. The researchers found that the waves of brain activity recorded both during seizures and between seizure episodes originated from the same location in the brain. This suggests that brain activity recorded between seizure episodes could both inform our understanding of how epileptic activity spreads through the brain, and aid clinical identification of the source of epileptic activity.
Building a Repertoire of Antiviral Immune Responses in MS
By Nina Lichtenberg, Ph.D.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. In MS, the immune system attacks myelin, a protective layer that covers nerve cells, leading to vision loss, muscle weakness, fatigue, and other debilitating symptoms. Studies have pointed to viruses as “triggers” of MS, including measles, mumps, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), but the link between these viruses and MS is just starting to emerge.
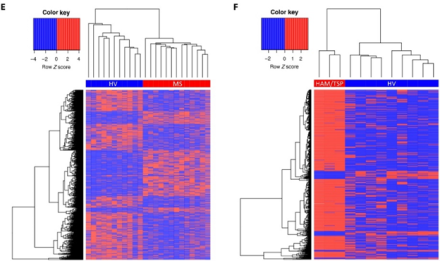
To explore this connection, Dr. Steven Jacobson and his team used VirScan, a powerful approach used to test for immune markers of hundreds of viruses that currently or previously infected a person. In the study, researchers collected and analyzed blood and cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) from 13 people with MS, three with a post-viral neurological condition called HAM/TSP, and 12 healthy controls. The results revealed key differences in antibody levels, such as increases in specific immune responses to multiple viruses, including EBV, in MS and HAM/TSP compared to healthy controls. Further analysis identified novel antibody profiles or immunological signatures in people with both conditions, which could help inform diagnoses and disease classification.
Although researchers did not find a virus-specific immune response unique to MS, the study adds to evidence that viral infections are linked to MS and other neurological conditions. Findings also demonstrate the utility of viral profiling may provide insight into potential biomarkers and future therapies. Larger studies will determine if the antibody profiles are disease-specific or can predict disease outcomes.
Archive
A Lasting Legacy
James “Jim” Wendel passed away in 2020 after a lifelong struggle with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, an inherited neurological disorder that causes nerve damage, primarily to peripheral nerves controlling muscles in the hands, arms, legs, and feet. A civil engineer, Mr. Wendel made a substantial contribution through the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) in support of the work of Dr. Carsten Bönnemann – head of the Neuromuscular and Neurogenetic Disorders of Childhood Section. Dr. Bönnemann’s research focuses on discovering the genetic causes of early onset neurological disorders in young children and developing precision therapies that target the defective genes. This legacy gift will enable Dr. Bönnemann and his team of researchers at NINDS to take one subtype of congenital neuromuscular disease where a unique genetic mutation has already been identified and test a potential therapy for that specific condition. Click here to read more.
Functional modules in the human temporal lobe found at the micro scale
Most of us are familiar with the different lobes of the brain that control general functions, like vision, motor control, and abstract thinking. But there is growing evidence for other layers of organization within each of these regions. Novel work is exploring this network organization in the temporal cortex, a region important for providing context to faces and other objects that a person sees in their visual field.
Dr. Julio Chapeton, research fellow in the Functional Neurosurgery Section at NINDS, set out to explore the human temporal cortex for evidence of smaller, organized regions that have unique processing functions. Small-scale recordings were performed in a group of patients with epilepsy who were having surgery to understand their brain’s epileptic regions. A small (4x4 millimeters, mm) grid of recording electrodes was placed in a non-epileptic region to analyze the activity of both the surface and deeper layers of the cortex. These recordings were performed while the patients viewed sets of images displaying persons, places, objects, and animals.
These recordings revealed small networks of neurons that activated together during presentations of the same image at different times throughout the experiment. This suggests that within the human temporal cortex there are very small functional modules, approximately 1.3 mm in diameter. These modules provide evidence of organization in the temporal cortex at the micro-scale. Similar observations have been made before in the human visual cortex; this new work in the temporal cortex indicates that functional modules may be a general property of the human cortex.
NIH study in mice provides insight into how brain activity is fine-tuned
Research explores how new information is consolidated across the sleep-wake cycle
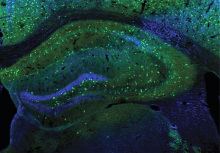
Using a mouse model, researchers have discovered a new daily rhythm in a type of synapse that dampens brain activity. Known as inhibitory synapses, these neural connections are rebalanced so that we can consolidate new information into long-lasting memories during sleep. In the study, Kunwei Wu, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Lu’s lab, examined what happens at inhibitory synapses during sleep and wakefulness in mice. Their experiments suggest that the accumulation of GABAA receptors during wakefulness may be key to building stronger, more efficient inhibitory synapses, a fundamental process known as synaptic plasticity.
The findings, published in PLOS Biology, may help explain how subtle synaptic changes enhance memory in humans. Humans and mice share similar neural circuits underlying memory storage and other essential cognitive processes. This mechanism may be a way for inhibitory inputs to precisely control the ebb and flow of information between neurons and throughout entire brain networks.
Because inhibition is essential for nearly every aspect of brain function, this study could contribute to helping scientists understand not just sleep-wake cycles, but neurological disorders rooted in abnormal brain rhythms, such as epilepsy.
Census "matters": glial cells are shaped by their neighbors
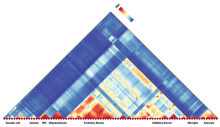
The brain and spinal cord can be divided into “grey matter” and “white matter” regions. We’ve learned a lot about the cell types found in the gray matter by studying the brains of rodents. However, rodent brains have relatively little white matter, limiting our understanding of its detailed composition in healthy brains and of the white matter abnormalities that are hallmark of many neurological disorders. To address this gap, Drs. Jing-Ping Lin and Daniel Reich turned to the common marmoset, a powerful and emerging neurological model system that genetically bridges rodents and humans and has high content of white matter. They created a rich dataset by rigorously surveying the transcriptomes (all the gene readouts) of 0.5 million cells over 19 regions of the central nervous system. They carefully annotated this dataset to create a marmoset brain cell atlas resource, “Callithrix jacchus Primate Cell Atlas” (CjPCA), which is freely available through https://cjpca.ninds.nih.gov and is designed to inform future studies in evolutional, developmental, and pathological neurobiology. They also conducted initial analyses of these data, identifying the molecular signatures and spatial distributions of 87 distinct cell types in the marmoset brain and strong differences between glial cells found in the white and gray matter. Finally, they also explored how developmental processes, local microenvironment, and disease states shape these distinct cell types. This unique data set is expected to yield many other new insights, and the methods used to obtain it can be used as a framework for studying brain cell types in other regions or species.
Intrinsic Potential for Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury
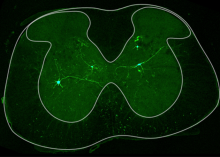
Spinal cord injury is a traumatic event that affects the intricate ecosystem of neurons and supporting cells in the spinal cord, often leading to paralysis. After spinal cord injury, “spared” tissue below the lesion contains undamaged cells that could augment or support recovery. However, targeting these cells requires a clearer understanding of their injury responses and capacity for repair.
In a recent publication, Dr. Ariel Levine and Kaya Matson profiled how each cell type in the spared tissue of the spinal cord changes over time after injury. They created an atlas of cell types, ranging from acute to chronic timepoints (https://seqseek.ninds.nih.gov/spinalcordinjury). The size and scope of this study allowed for identification of rare cells with the potential to support recovery. They identified neurons which had a gene signature of regeneration, normally only seen in peripheral neurons that regenerate after injury, and not in the central nervous system which is much more limited in its regenerative capability. The researchers identified the neurons with the pro-regenerative gene signature, including spinocerebellar neurons. They labeled spinocerebellar neurons and found that they remodeled after injury. This work shows the inherent potential for plasticity after injury in neurons important for coordination and movement after spinal cord injury.
GRN mutations are associated with Lewy body dementia
Lewy body dementia (LBD) is a common form of dementia in the elderly population, affecting approximately 1.4 million people in the United States. LBD can cause symptoms that include visual hallucinations, changes in attention, and slowing of movement, among others. The cause of LBD is poorly understood, but genetic factors are thought to play a role.
In a recent study, Dr. Sonja Scholz and her team examined the genomes from about 2,600 LBD patients and 4,000 controls who did not have a history of cognitive or neurological conditions. They were specifically looking at the GRN gene, which has been shown to be important in several cellular processes. These include cell growth, inflammation, and protein metabolism. Mutations in GRN have been previously linked to another serious neurological disease, frontotemporal dementia. Given that frontotemporal dementia and LBD share some overlap in their symptom presentation, there was interest in whether LBD cases would also be linked to GRN mutations.
When reviewing the genomes from the LBD patients, they discovered that these GRN mutations were in fact more common compared to the healthy control group. A further review of tissue samples from some of the mutation carriers also confirmed that the patients indeed showed features of both LBD and frontotemporal dementia. This suggests that molecular relationships may exist between these two understudied types of dementia, opening potential avenues for using genome sequencing as a diagnostic tool. In addition, this information may help to improve disease modeling and therapy development. As novel therapies targeting the GRN gene are already in the clinical trials stage, the study raises hopes that future trials could be expanded to LBD.
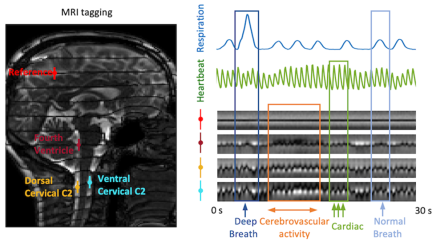
Cerebrovascular activity has major impact on cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics
This finding indicates an important role of cerebrovascular activity in CSF pulsations. Recently, it has been proposed that pulsatile movement of CSF may assist in the clearance of metabolic waste products from the brain that have been linked to neurodegeneration. Together, this suggests a potential link between impaired vascular reactivity and compromised waste clearance.
Noxa deregulation drives hormone secreting pituitary adenomas
The small size of the pituitary gland belies its important role as master regulator of many of the hormones that our body needs to function properly. Tumors on the pituitary can occur in up to 10% of the general population. These tumors - called adenomas - are benign, in that they do not cause cancer. However, they can substantially disrupt the normal functions of the pituitary gland, with big consequences. Cushing’s disease is one such consequence. In this disease, the pituitary adenoma causes too much cortisol (a stress hormone) to be made, leading to a plethora of physical changes and systemic complications. While treatments exist, they cannot fully reverse the effects of ongoing cortisol overproduction. The best way to treat Cushing’s disease would be to stop the overproduction of cortisol at the source, by eliminating the pituitary adenoma.
Dr. Prashant Chittiboina, an investigator in the Neurosurgery Unit for Pituitary and Inheritable Diseases, studies the basic biology of pituitary adenomas to identify new ways to eliminate those that cannot be removed surgically. In a recently published study, his team collected cells from the adenomas and adjacent normal tissue of 34 patients during surgery. Using modern high-throughput molecular characterization techniques, they created an atlas of cell normal and abnormal pituitary cell types, and used this information to reveal a molecular signature unique to the adenoma cells. They showed that this molecular signature includes a trip-wire protein that should be toxic to the adenoma cells. However, adenoma cells were able to destroy this protein and protect their survival. Using a new mouse cell model, the group showed how to allow this trip-wire protein to accumulate in adenoma cells. To do this, the group used drugs that have already been approved for other conditions as pills. This study paves a smooth road to testing such treatments for Cushing’s disease in human patients.
“After publication, this work prompted a recent Nature Reviews Endocrinology article discussing these new mechanisms of Cushing disease that Dr. Chittioina and his team uncovered.”
Heterozygous PRKN mutations are common but do not increase risk of Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the second most common neurogenerative disease, causing symptoms such as tremor, bradykinesia, and gait problems. In general, 5-10% of cases are caused by a genetic mutation of a single gene, and therefore new therapies that can target these mutations may become important as future treatment options.
One potential target for gene therapy is PRKN, a gene that produces the protein Parkin. Parkin helps to rid the body of faulty or damaged mitochondria, which can wreak havoc on the health of cells, especially in the brain. Having mutations in both copies of PRKN causes PD. But does a single PRKN mutation also increase the risk of someone developing PD?
In a recent paper , Dr. Derek Narendra, Chief of the Inherited Movement Disorders Unit and a Lasker Clinical Research Scholar, investigated just this question. His team evaluated individuals with single PRKN mutations in two large groups of human research participants with available genetic data. One group reflected the general population and the other specifically included patients with PD.
Overall, they found that single PRKN mutations are common in the general population but occur as often in people with PD as those without PD. These results suggest that single PRKN mutations do not increase risk of PD. These findings will inform the counseling of patients with PD and their families, and help to better design gene therapy trials for PD.
Dr. Avindra Nath Investigates the Mysterious Ways Viruses Affect the Nervous System and is Featured on Global Documentary
The COVID-19 pandemic was not Avindra “Avi” Nath’s first face-off with an enigmatic, rapidly spreading virus. From the AIDS pandemic to the current pandemic, Dr. Nath is one of the world’s foremost experts on how viruses affect the brain. As the NINDS Clinical Director and the head of the Section of Infections of the Nervous System, he occupies a unique niche that requires expertise in two seemingly unrelated fields. “If you’re trained as a neuroscientist or neurologist, you understand the functions of the brain, but if you’re trained as a virologist, you study viruses, and there’s no way you would get exposed to the intricacies of the brain,” Dr. Nath explains. “I trained in both, so I was able to marry the two together.” Read more.
Dr. Nath was also featured on Here’s What We Know About COVID-19’s Impact on the Brain – a documentary produced by Science Magazine that focuses on the impact of COVID-19 in the brain, as well as novel therapeutic approaches to improve the symptoms of long COVID, such as autonomic rehabilitation, and an immune modulating drug trial awaiting regulatory approval. Renown scientists, like Dr. Nath, hope that the knowledge gained from long COVID will benefit those facing post-viral illnesses. You can watch the video in its entirety on YouTube.
Mechanisms of TMC1-related Hearing Loss may involve Alterations in Membrane Homeostasis
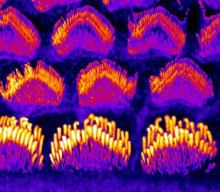
Sensory hair cells of the inner ear required for hearing and balance rely on the mechanoelectrical transduction (MET) channel complex to convey mechanical signals from sound or head movements into electrical impulses. Transmembrane-like channel 1 and 2 (TMC1 and TMC2) are thought to form the ion conduction pore of the MET channel, yet the distinctive roles of the two proteins and how TMC1 mutations cause hair cell death remain elusive.
In this article published in BioRxiv, Regulation of membrane homeostasis by TMC1 mechanoelectrical transduction channels is essential for hearing, Drs. Angela Ballesteros and Kenton Swartz discover that TMC1 controls membrane homeostasis initiated by inhibition of MET channels and that deafness-causing mutations in TMC1 lead to constitutive phosphatidylserine externalization that correlates with the deafness phenotype, suggesting that the mechanisms of TMC1-related hearing loss may involve alterations in membrane homeostasis. Read more.
Distinct Regulation of Tonic GABAergic Inhibition by NMDA Receptor Subtypes
A study published in Cell Reports, led by Dr. Kunwei Wu and team from Dr. Wei Lu’s lab found the differential modulation of tonic inhibition by NMDA receptor subtypes and reveal distinct roles of GluN2A- and GluN2B-NMDA receptors in regulating ɑ5-GABAAA receptor trafficking, tonic inhibition and its homeostatic plasticity in hippocampal neurons. They also demonstrate the regulation of tonic inhibition by NMDA receptors in a kainate-induced seizure model. As dysregulation of tonic inhibition has been shown to be a mechanism underlying a number of pathological brain states, these findings provide insight into crosstalk between glutamatergic and GABAergic systems, as well as how dysregulation of this crosstalk could be involved in epileptic conditions. Read the full publication.
Signaling from Neighboring Cells Provides Power Boost within Axons
NIH study identifies possible target for certain neurodegenerative disorders. Neurons require mechanisms to maintain ATP homeostasis in axons, which are highly vulnerable to bioenergetic failure. Recent work from Dr. Zu-Hang Sheng and his team offers insights that advance our understanding of axonal energy metabolism; energy deficits are associated with a wide range of neurological disorders. Read full press release.
Adenosine A2A Receptor Activation Enhances Blood–Tumor Barrier Permeability in a Rodent Glioma Model
In a study by Dr. Sadhana Jackson and colleagues published in AACR Molecular Cancer Research, researchers characterize the time-dependent impact of regadenoson on brain endothelial cell interactions and paracellular transport, using mouse and rat brain endothelial cells and tumor models. Collectively, these findings demonstrate regadenoson's ability to induce brain endothelial structural changes among malignant glioma cells to increase BTB permeability. Read more.
Scientists Discover a New Molecular Pathway Shared by two Neurodegenerative Disorders
Finding provides a possible therapeutic target for ALS and FTD. Researchers from two independent research teams have discovered how the mislocalization of a protein, known as TDP-43, alters the genetic instructions for UNC13A, providing a possible therapeutic target that could also have implications in treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and other forms of dementia. Read press release.
Scientists Discover a New Form of ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a heterogeneous neurodegenerative disorder that results in loss of voluntary muscle strength and movement. ALS usually affects middle-aged adults and progresses rapidly, but in the recent study Childhood amyotrophic lateral sclerosis caused by excess sphingolipid synthesis, published in Nature Medicine, an international team reported a new and unique, rare form of ALS with onset in young children followed by a somewhat slower but equally progressive course.
Identifying this new form of ALS was just the start towards a deeper understanding of the mechanisms driving the disease. Read the full NINDS press release, NIH Record article, and see international press coverage of this study.
Changing How We Understand the Role of Genes and the Microbiome in Aging
Drs. Arvind Shukla, Kory Johnson, and Senior Investigator Ed Giniger are changing how we understand the role of genes and the microbiome in aging. Published in iScience, Common features of aging fail to occur in Drosophila raised without a bacterial microbiome reports on unexpected differences in gene expression between flies raised under normal conditions or in the absence of bacteria (with antibiotics). A large body of research has identified many genes that change their expression as an animal ages, and these genes are considered hallmarks of the aging process. In this study, however, the team found that 70% of these classic age-related genes did not change their expression over time when the flies were raised without bacteria, indicating that these genes are actually responding to the microbe-rich environment, rather than the animal's internal aging clock. Read the full NINDS press release, or see the buzz around the story on twitter!
Infection Hinders Blood Vessel Repair following Traumatic Brain or Cerebrovascular Injuries
Researchers at the NNINDS led by Dr. Dorian McGavern have found a possible explanation for why some patients recover much more poorly from brain injury if they later become infected. The findings were published in Nature Immunology. Making use of a mouse model for mild TBI (mTBI) that they had developed previously, the team of researchers discovered that viral, fungal, or a mimic for bacterial infections all impacted blood vessel repair within the meninges. When they looked closer, they observed that some cells of the immune system no longer moved into the site of the injury, which occurred in the uninfected animals, suggesting they were responding to systemic infection. Read press release.
Building a Cellular Blueprint of MS Lesions
Investigators build a cellular blueprint of multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions providing a better understanding of the entire network of cells. Danny Reich and his team had a fascinating paper recently published in Nature, A lymphocyte–microglia–astrocyte Axis in Chronic Active Multiple Sclerosis. Chronic lesions with inflamed rims, or “smoldering” plaques, in the brains of people with MS have been linked to more aggressive and disabling forms of the disease. Using brain tissue from humans, Dr. Reich and colleagues built a detailed cellular map of chronic MS lesions, identifying genes that play a critical role in lesion repair and revealing potential new therapeutic targets for progressive MS. Read the full press release.
Why Short Breaks Help Us Learn
A NINDS team led by Senior Investigator Dr. Leonardo Cohen and staff scientist Dr. Ethan Buch recently published a study mapping out the brain activity that occurs when we learn a new skill and discovered why taking short breaks from practice is a key to learning. In a recent publication appearing in Cell Reports, the researchers used magnetoencephalography to record the brain waves of volunteers as they practiced rapidly typing a code and during short rests between practice. A machine learning approach allowed them to decipher the brain wave activity associated with typing a code. During rests between periods of practice, the brains of healthy volunteers rapidly and repeatedly replayed much faster, compressed versions of the brain waves that occurred during active typing practice. The more a volunteer's brain replayed the pattern during rest, the better they performed during subsequent practice sessions, suggesting rest strengthened the memory of the typing skill.
The study also identified the brain regions where this replay occurs. The researchers hope that the study sheds light not only on the role that rest can play in normal skill learning, but also points to strategies for enhancing skill learning, including as part of rehabilitation interventions after brain injury. Read the full press release, or listen to a short interview with Drs. Cohen and Buch that appeared in the Scientific American.
Distinguishing Type II Focal Cortical Dysplasias from Normal Cortex: A Novel Normative Modeling Approach
Seizure outcomes in epilepsy surgery are better when epileptogenic lesions are identified. There is no widely available automated method for aiding with detection of subtle focal cortical dysplasia lesions. In this study, the researchers describe a novel approach for aiding with detection of these lesions using structural MRI. Detection of subtle dysplastic lesions in individual patients undergoing epilepsy surgery has the ability to significantly improve seizure outcomes in these patients. Read more.
Genome Sequencing Analysis Identifies New Loci Associated with Lewy Body Dementia and Provides Insights into its Genetic Architecture
Led by Dr. Scholz, a team of investigators identified novel risk loci associated with this devastating disease, and they were able to show molecular relationships between Lewy body disease (LBD), Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. The genome data described in this study constitute the largest sequencing effort in LBD to date and are designed to accelerate the pace of discovery in dementia research. Read more.
An Epilepsy-Associated GRIN2A Rare Variant Disrupts CaMKIIα Phosphorylation of GluN2A and NMDA Receptor Trafficking
In a project led by Dr. Marta Mota Vieira, we characterized a novel CaMKIIα phosphorylation site, S1459, in the GluN2A subunit of NMDA receptors. Phosphorylation of this residue promotes trafficking of the receptor to the neuronal surface, modulates receptor interactions with trafficking and scaffold proteins. This provides a previously unappreciated link between GluN2A-specific NMDA receptor function and the important synaptic signaling kinase CaMKIIα. Importantly, we found that an epilepsy-associated variant (S1459G) identified at the same residue decreases synaptic expression of NMDA receptors, spine density, and spontaneous post-synaptic currents, consistent with the epilepsy-related variant being a loss-of-function mutation. Read more.
Evidence for a Stereoselective Mechanism for Bitopic Activity by Extended-Length Antagonists of the D3 Dopamine Receptor
Investigators performed a high-throughput screen of a small molecule library to identify a D3R-selective agonist with low cross-reactivity with the closely related D2R. We then conducted a comprehensive structure–activity relationship investigation using iterative medicinal chemistry to establish the structural determinants for potency, efficacy, and selectivity of the agonist at the D3R. An optimized lead compound, ML417, was identified that promotes potent and selective D3R activation. ML417 shows almost no cross reactivity with other receptors, indicating it is globally selective for the D3R. They also identified amino acid residues in the D3R DAR that uniquely interact with ML417, explaining the compound’s unprecedented selectivity. In follow-up studies, ML417 was found to exhibit neuroprotection against toxin-induced neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Read more.