Background
NINDS recently set up the quantitative MRI (qMRI) Core facility under the supervision of the Core Director, Dr. Govind Bhagavatheeshwaran. The primary goal of the core is to provide PIs access to research MRI resources developed within and outside NINDS, and to assist in their implementation as endpoints in clinical trials of neurological diseases.
Contact Information
Govind Ghagavatheeshwaran, Ph.D.
Phone: 301-402-6391
E-mail: govind.bhagavatheeshwaran@nih.gov
Scope of the Facility
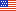
The qMRI Core will primarily focus on groups that lack staff well trained in acquisition and processing of MRI data. The Core facility will help these groups implement the pulse sequences and provide the support needed to perform image analysis in well defined, time limited projects. A few examples of endpoints implemented at the core facility are shown below in Figure 1. The Core facility personnel are also available to work with investigators and their team to develop new markers.
In addition, the core will offer its services for postmortem MRI of the human brain and spinal cord, as well as for MRI-guided tissue slicing using a 3D printed cutting box if requested. There is a growing demand to image fixed human brain, especially entire autopsy specimens. The expertise necessary to acquire and interpret high resolution images from large brain specimens available in-house at the q-MRI Core will be provided to the broader NINDS and NIH community.