Background
The Flow & Imaging Cytometry Core Facility provides intellectual, technical, training and collaborative support to NINDS and other intramural.
investigators in both basic and clinical research programs requiring seamless and productive use of conventional flow cytometry, imaging flow cytometry, preparative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and in situ cytometric imaging techniques to assay cell biology at the molecular, subcellular and cellular levels, as specified by the investigator. Depending on the investigator's requirements, the Facility provides high-throughput screening of cells and assaying of their specific biological properties, in addition to preparative sorting of purified cell populations and/or subpopulations of interest, based on one of more specific cellular/subcellular parameters, as specified by the investigator.
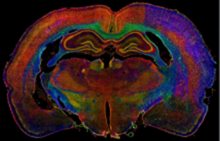
Facility staff is also continuously engaged in research and development of novel methodological approaches to comprehensively study systems biology in the brain using animal models for specific neurological and neurodegenerative disorders (ischemic and traumatic brain injuries, brain tumors, aging brain, select transgenic animal models of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases, etc.), for which they combine up to 100-plex biomarker immunohistology screening with multi-spectral fluorescence imaging and multi-parametric big image data analyses.
Contact Infomration
Dragan Maric, Ph.D., Core Director
Phone: (301) 402-1406
E-mail: maricd@ninds.nih.gov
Andrea Sedlock, M.S., Biologist
Phone: (301) 402-6934
E-mail: andreasedlock@mail.nih.gov
Scope of the Core Facility
The primary mission of the Facility is to provide intellectual, technical, collaborative and new application research and development support to NINDS and other intramural investigators in both basic and clinical research programs requiring the use of high-throughput conventional flow cytometry (CFC), imaging flow cytometry (IFC), preparative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and multi-spectral in situ cytometric imaging (ISCI). The Facility currently provides routine use of CFC, IFC, FACS and ISCI applications in assaying a multitude of biological properties at the cellular, subcellular and molecular levels, as specified by the investigator.
Critical to these activities is the research and development of a wide variety of novel, customized and standardized multiplex biomarker screening protocols using unique combinations of fluorescent reporters of interest, including those identifying different stages of cell proliferation and differentiation, as well as different types of cell death (i.e., apoptotic, necrotic, cytotoxic, autophagy), in addition to those assaying functional gene expression and cell signaling. The aim of these protocols is to maximize the simultaneous detection and quantification of multiple biological properties per cell and its subcellular compartments (i.e., plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, synaptosomes, microvesicles, exosomes), utilizing an array of appropriate cell surface, cytoplasmic, nuclear, protein and gene expression biomarkers, as well as select physiological indicator dyes (potentiometric, calcium, pH, live/dead), linked to fluorescent endpoints.
Depending on the investigator’s requirements, the Facility provides high-throughput screening of cells and assaying of their specific biological properties, in addition to preparative sorting of purified cell populations and/or subpopulations of interest, based on one or more specific cellular/subcellular parameters, as specified by the investigator. Additional responsibilities of the Facility personnel include regular maintenance and technological upgrades of all instruments that are managed by the Facility, as well as daily instrument alignment and calibration, setting up sample quality controls and standardization, and enabling seamless data acquisition and analysis, presentation and interpretation of the resulting findings to the investigator, and, if requested by the investigator, manuscript preparation and critical review.
Core Facility Equipment
The Facility provides seamless utilization of the following equipment: MoFlo Astrios cell sorter (Beckman Coulter), ImageStreamX flow cytometer (Amnis Corporation) and AxioImager.Z2 10-channel wide-field fluorescence microscope with motorized scanning stage (Carl Zeiss). The optical configurations and services currently provided with each instrument are listed below:
MoFlo Astrios

|
Services |
- conventional flow cytometry (CFC) and preparative cell sorting (FACS) |
|
Excitation |
- 7 air-cooled lasers (355, 405, 488, 532, 561, 592, 640 nm) |
|
Emission |
- up to 30 (peak emissions ranging from near-UV to near-IR spectrum) |
|
Acquisition |
- up to 1x105 cells/sec, up to 1x109 cells per acquisition |
|
Sorting |
- simultaneous 6-way sorting (enrich, pure, single cell) |
|
Bioassays |
- cell cycle and mitosis (DNA content, BrdU incorporation) |
ImageStreamX Flow Cytometer

|
Services |
- imaging flow cytometry (IFC) |
|
Excitation |
- up to 7 air-cooled lasers (3 currently available: 405, 488, 658 nm) |
|
Emission |
- up to 10 (peak emissions ranging from near-UV to near-IR spectrum) |
|
Dyes |
- DAPI, FITC, PE, PE-TR, PE-Cy5, PE-Cy7, Pacific Blue, Pacific Orange |
|
Acquisition |
- up to 2x103 imaged cells/sec, up to 1x105 imaged cells per acquisition |
|
Bioassays |
- cell cycle and mitosis (DNA content, BrdU incorporation, stages of cell mitosis) |
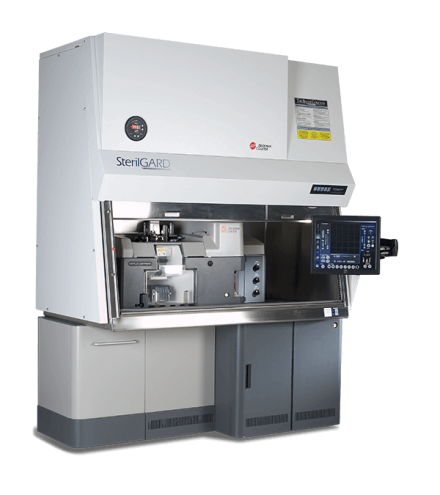
AxioImager.Z2 Scanning Widefield Fluorescence Microscope
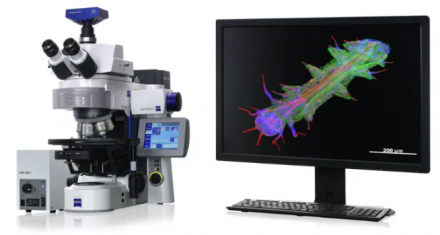
|
Services |
- multispectral in situ cytometric imaging (ISCI) Excitation |
|
Excitation |
- mercury arc lamp (light filtered using 10 spectrally-compatible exciter filters) |
|
Emission |
- up to 10 (peak emissions ranging from near-UV to near-IR spectrum) |
|
Dyes |
- Alexa 350, 405, 430, 488, 546, 594, 647, 700, 750, IRDye800CW, PerCP |
|
Acquisition |
- scan areas up to 1 cm2 in brightfield and up to 10 fluorescence channels |
|
Bioassays |
- cell cycle and mitosis (DNA content, BrdU incorporation, stages of cell mitosis) |
How to Use the Core Facility
To schedule an appointment, please contact the Core Director by e-mail (maricd@ninds.nih.gov), phone (301-402-1406) or stop by the Core Facility (Building 10, Room 5S-241) to sign in the scheduling calendar. If new to flow and imaging cytometry or unsure how to best utilize the resources available at the Core, the Core Director will be available to assist the investigator using the following workflow:
Step 1 - Initial consultation with initiating investigator to determine optimal experimental designs tailored to investigator’s interests. The investigator is also familiarized with all the bioassays that have been standardized and are routinely available at the Core Facility.
Step 2 - If standard bioassays currently provided by the Core are not adequate, the Core Director will work with the investigator to conduct new research and development of customized applications to meet the investigator’s requirements.
Step 3 - Pilot experiments are carried out first to empirically optimize the bioassays using quality controls for verifying sample integrity and identifying specific endpoints of fluorescent reporters, while at the same time discriminating against possible artifacts and non-specific signals.
Step 4 - Once optimized and standardized, the bioassays are available to the investigator for routine use. If problems are encountered with the instrumentation, samples or bioassays, the Core Director will be available to troubleshoot the problems and provide optimal solutions to correct the problems.
Selected Publications Using the Core
- Pratt D, Dominah G, Lobel G, Obungu A, Lynes J, Sanchez V, Adamstein N, Wang X, Edwards NA, Wu T, Maric D, Giles AJ, Gilbert MR, Quezado M, Nduom EK (2018) Programmed death ligand 1 is a negative prognostic marker in recurrent isocitrate dehydrogenase-wildtype glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 2018 Jul 12. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy268. PMID: 30011045.
- Hao S, Song H, Zhang W, Seldomridge A, Jung J, Giles AJ, Hutchinson MK, Lita A, Larion M, Maric D, Abu-Asab M, Kramp T, Camphausen K, Zhuang Z, Gilbert MR, Park DM (2018) Protein phosphatase 2A inhibition enhances radiation sensitivity and reduces tumor growth in chordoma. Neuro-Oncology 2018 May 18;20(6):799-809. PMID: 29294092.
- Sapio MR, Neubert JK, LaPaglia DM, Maric D, Keller JM, Raithel SJ, Rohrs EL, Anderson EM, Butman JA, Caudle RM, Brown DC, Heiss JD, Mannes AJ, Iadarola MJ (2018) Pain control through selective chemo-axotomy of centrally projecting TRPV1+ sensory neurons. J Clin Invest 2018 Apr 2;128(4):1657-1670. doi: 10.1172/JCI94331. Epub 2018 Mar 19. PMID: 29408808.
- Su YT, Chen R, Wang H, Song H, Zhang Q, Chen LY, Lappin H, Vasconcelos G, Lita A, Maric D, Li A, Celiku O, Zhang W, Meetze K, Estok T, Larion M, Abu-Asab M, Zhuang Z, Yang C, Gilbert MR, Wu J (2018) Novel targeting of transcription and metabolism in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2018 Mar 1;25(5):1124-1137. PMID: 29254993.
- Ho WSC, Sizdahkhani S, Hao S, Song H, Seldomridge A, Tandle A, Maric D, Kramp T, Lu R, Heiss JD, Camphausen K, Gilbert MR, Zhuang Z, Park DM (2018) LB-100, a novel protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) inhibitor, sensitizes malignant meningioma cells to the therapeutic effects of radiation. Cancer Lett 2018 Feb 28;415:217-226. PMID: 29199006.
- Bernstock JD, Ye DG, Griffin A, Lee YJ, Lynch J, Latour LL, Friedman GK, Maric D, Hallenbeck JM (2018) Cerebral ischemia increases small ubiquitin-like modifier conjugation within human penumbral tissue: radiological-pathological correlation. Front Neurol. 2018 Jan 12;8:738. PMID: 29375471.
- Bernstock JD, Ye D, Gessler FA, Lee YJ, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, Baumgarten P, Johnson KR, Maric D, Yang W, Kogel D, Pluchino S, Hallenbeck JM (2017) Topotecan is a potent inhibitor of SUMOylation in glioblastoma multiforme and alters both cellular replication and metabolic programming. Sci Rep 7:7425. PMID: 28785061.
- Lu J, Chatain GP, Bugarini A, Wang X, Maric D, Walbridge S, Zhuang Z, Chittiboina P (2017) Histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA is a novel, promising treatment for Cushing's Disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102: 2825-2835. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00464. PMID: 28505327.
- Pandya H, Shen MJ, Ichikawa DM, Sedlock A, Choi Y, Johnson KR, Kim G, Brown MA, Elkahloun A, Maric D, Sweeney CL, Gossa S, Malech HL, McGavern DB, Park JK (2017) Differentiation of human and murine induced pluripotent stem cells to microglia-like cells. Nat Neurosci 20:753-759. PMID: 28253233.
- Sizdahkhani S, Feldman MJ, Piazza MG, Ksendzovsky A, Edwards NA, Ray-Chaudhury A, Maric D, Merrill MJ, Pacak K, Zhuang Z, Chittiboina P (2017) Somatostatin receptor expression on von Hippel-Lindau-associated hemangioblastomas offers novel therapeutic target. Sci Rep 7:40822. PMID: 28094316.
Additional Publications
- Bott LC, Salomons FA, Maric D, Liu Y, Merry D, Fischbeck KH, Dantuma NP (2016) The polyglutamine-expanded androgen receptor responsible for spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy inhibits the APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase complex. Sci Rep 6:27703.
- Komori M, Lin YC, Cortese I, Blake A, Ohayon J, Cherup J, Maric D, Kosa P, Wu T, Bielekova B (2016) Insufficient disease inhibition by intrathecal rituximab in progressive multiple sclerosis. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 3:166-179.
- Ho WS, Feldman MJ, Maric D, Amable L, Hall MD, Feldman GM, Ray-Chaudhury A, Lizak MJ, Vera JC, Robison RA, Zhuang Z, Heiss JD (2016) PP2A inhibition with LB100 enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity and overcomes cisplatin resistance in medulloblastoma cells. Oncotarget 7:12447-12463.
- Bernstock, JD, Lee YJ, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, Southall N, Johnson KR, Maric D, Volpe G, Kouznetsova J, Zheng W, Pluchino S, Hallenbeck JM (2016) A novel quantitative high-throughput screen identifies drugs that both activate SUMO conjugation via the inhibition of microRNAs 182 and 183 and facilitate neuroprotection in a model of oxygen and glucose deprivation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:426-441.
- Li W, Lee MH, Henderson L, Tyagi R, Bachani M, Steiner J, Campanac E, Hoffman DA, von Geldern G, Johnson K, Maric D, Morris HD, Lentz M, Pak K, Mammen A, Ostrow L, Rothstein J, Nath A (2015) Human endogenous retrovirus-K contributes to motor neuron disease. Sci Transl Med 7:307ra153.
- Feldman M, Piazza MG, Edwards NA, Ray-Chaudhury A, Maric D, Merrill MJ, Zhuang Z, Chittiboina P (2015) Somatostatin receptor expression on VHL-associated hemangioblastomas offers novel therapeutic target. Neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 62 Suppl 1:209-210.
- Absinta M, Vuolo L, Rao A, Nair G, Sati P, Cortese IC, Ohayon J, Fenton K, Reyes-Mantilla M, Maric D, Calabresi PA, Butman JA, Pardo CA, Reich DS (2015) Gadolinium-based MRI characterization of leptomeningeal inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 85:18-28.
- Salvucci O, Ohnuki H, Maric D, Hou, X, Li X, Yoon SO, Segarra M, Eberhart CG, Acker-Palmer A, Tosato G (2015) EphrinB2 controls vessel pruning through STAT1-JNK3 signaling. Nat Commun 6:6576.
- Brachman RA, Lehmann ML, Maric D, Herkenham M (2015) Lymphocytes from chronically stressed mice confer antidepressant-like effects to naive mice. J Neurosci 35:1530-1538.
- Goswami SC, Mishra SK, Maric D, Kaszas K, Gonnella GL, Clokie SJ, Kominsky HD, Gross JR, Keller JM, Mannes AJ, Hoon MA, Iadarola MJ (2014) Molecular signatures of mouse TRPV1-lineage neurons revealed by RNA-Seq transcriptome analysis. J Pain 15:1338-1359.
- Ohnuki H, Jiang K, Wang D, Salvucci O, Kwak H, Sánchez-Martín D, Maric D, Tosato G (2014) Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells activate Dll4/Notch/TGF-β signaling to drive malignant progression. Cancer Res 74:2038-2049.
- Johnson TP, Patel K, Johnson KR, Maric D, Calabresi PA, Hasbun R, Nath A (2013) Induction of IL-17 and non-classical T-cell activation by HIV-Tat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:13588-13593.
- Hunsberger JG, Fessler EB, Chibane FL, Leng Y, Maric D, Elkahloun AG, Chuang DM (2013) Mood stabilizer-regulated miRNAs in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases: identifying associations and functions. Am J Transl Res 5:450-464.
- Segarra M, Ohnuki H, Maric D, Salvucci O, Hou X, Kumar A, Li X, Tosato G (2012) Semaphorin 6A regulates angiogenesis by modulating VEGF signaling. Blood 120:4104-4115.
- Gasperini P, Espigol-Frigole G, McCormick PJ, Salvucci O, Maric D, Uldrick TS, Polizzotto MN, Yarchoan R, Tosato G (2012) Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus promotes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition through Notch-dependent signaling. Cancer Res 72:1157-1169.
- Rudenko IN, Kaganovich A, Hauser DN, Beylina A, Chia R, Ding J, Maric D, Jaffe H, Cookson MR (2012) The G2385R variant of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 associated with Parkinson’s disease is a partial loss-of-function mutation. Biochem J 446:99-111.
- Harberts E, Yao K, Wohler JE, Maric D, Ohayon J, Henkin R, Jacobson S (2011) Human herpesvirus-6 entry into the central nervous system through the olfactory pathway. PNAS 108:13734-13739.
- Lee Y-J, Mou Y, Maric D, Klimanis D, Auh S, Hallenbeck J (2011) Elevated global SUMOylation in Ubc9 transgenic mice protects their brains against focal cerebral ischemic damage. PLoS One 6(10):e25852.
- Wuchty S, Arjona D, Li A, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, Zhang A, Maric D, Anolik R, Zenklusen JC, Fine HA (2011) Prediction of associations between microRNAs and gene expression in glioma biology. PLoS One 6(2):e14681.
- Edwards LA, Woolard K, Son MJ, Li A, Lee J, Ene C, Mantey SA, Maric D, Song H, Belova G, Jensen RT, Zhang W, Fine HA (2011) Effect of brain- and tumor-derived connective tissue growth factor on glioma invasion. J Natl Cancer Inst 103:1162-1178.
- Wuest S, Han S, Martin J, Maric D, Bielekova B (2011) Vital role for IL-2 trans-presentation in DC-mediated T cell activation in humans as revealed by daclizumab therapy. Nature Medicine 17:604-609.
- Bogoslovsky T, Spatz M, Chaudhry A, Maric D, Luby M, Frank J, Warach S (2011) Stromal derived factor-1a correlates with circulating endothelial progenitor cells and with acute lesion volume in stroke patients. Stroke 42:618-625.
- Suen DF, Narendra DP, Tanaka A, Manfredi G, Youle RJ (2010). Parkin overexpression selects against a deleterious mtDNA mutation in heteroplasmic cybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:11835-11840.
- Fukunaga M, Li TQ, van Gelderen P, de Zwart JA, Shmueli K, Yao B, Lee J, Maric D, Aronova MA, Zhang G, Leapman RD, Schenck JF, Merkle H, Duyn JH (2010) Layer-specific variation of iron content in cerebral cortex as a source of MRI contrast. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:3834-3839.
- Zheng YL, Li BS, Rudrabhatla P, Shukla V, Amin ND, Maric D, Kesavapany S, Kanungo J, Pareek TK, Takahashi S, Grant P, Kulkarni AB, Pant HC (2010) Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 at Thr187 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 modulates neural stem cell differentiation. Mol Biol Cell 21:3601-3614.
- Chen BS, Roche KW (2009) Growth factor-dependent trafficking of cerebellar NMDA receptors via protein kinase B/Akt phosphorylation of NR2C. Neuron 62:471-478.
- Son MJ, Woolard K, Nam DH, Lee J, Fine HA (2009) SSEA-1 is an enrichment marker for tumor-initiating cells in human glioblastoma. Cell Stem Cell 4:440-452.
- Lee Y-J, Castri P, Bembry J, Maric D, Hallenbeck J (2009) SUMOylation participates in induction of ischemic tolerance. J Neurochem 109:257-267.
- Ishibashi S, Maric D, Mou Y, Ohtani R, Ruetzler C, Hallenbeck JM (2009) Mucosal tolerance to E-selectin promotes the survival of newly generated neuroblasts via regulatory T cell induction after stroke in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:606-620.
- Oh U, Blevins G, Griffith C, Richert N, Maric D, Lee CR, McFarland H, Jacobson S (2009) Regulatory T cells are reduced during anti-CD25 antibody treatment for multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 66:471-479.
- Sumner JP, Shapiro EM, Maric D, Conroy R, Koretsky AP (2009) In vivo labeling of adult neural progenitors for MRI with micron sized particles of iron oxide: Quantitation of labeled cell phenotype. Neuroimage 44:671-678.
- Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard, K, Donin NM, Li A, Cheng CH, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, Kim MS, Totonchy M, Cusack T, Ene C, Ma H, Su Q, Zenklusen JC, Zhang W, Maric D, Fine HA (2008) Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenic protein pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells. Cancer Cell 13:69-80.
- Kotliarova S, Pastorino S, Kovell LC, Kotliarov Y, Song H, Zhang W, Bailey R, Maric D, Zenklusen JC, Lee J, Fine HA (2008) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition induces glioma cell death through c-MYC, nuclear factor-kappaB, and glucose regulation. Cancer Res 68:6643-6651.
- Lau P, Verrier JD, Nielsen JA, Johnson KR, Notterpek L, Hudson LD (2008) Identification of dynamically regulated microRNA and mRNA networks in developing oligodendrocytes. J Neurosci 28:11720-11730.
- Lee Y-J, Miyake S, Wakita H, McMullen DC, Azuma Y, Auh S, Hallenbeck JM (2007) Protein SUMOylation is massively increased in hibernation torpor and is critical for the cytoprotection provided by ischemic preconditioning and hypothermia in SHSY5Y cells. J Cereb. Blood Flow Metab 27:950-962.
- Ngo TT, Peng T, Liang XJ, Akeju O, Pastorino S, Zhang W, Kotliarov Y, Zenklusen JC, Fine HA, Maric D, Wen PY, De Girolami U, Black PM, Wu WW, Shen RF, Jeffries NO, Kang DW, Park JK (2007) The 1p-encoded protein stathmin and resistance of malignant gliomas to nitrosoureas. J Natl Cancer Inst 99:639-652.
- Glod J, Kobiler D, Noel M, Koneru R, Lehrer S, Medina D, Maric D, Fine HA (2006) Monocytes form a vascular barrier and participate in vessel repair after brain injury. Blood 107:940-946.
- Chen BS, Braud S, Badger JD 2nd, Isaac JT, Roche KW (2006) Regulation of NR1/NR2C N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 281:16583-16590.
- Nielsen JA, Maric D, Lau P, Barker JL, Hudson LD (2006) Identification of a novel oligodendrocyte cell adhesion protein using gene expression profiling. J Neurosci 26:9881-9891.
- Nasu-Nishimura Y, Hurtado D, Braud S, Tang TT, Isaac JT, Roche KW (2006) Identification of an endoplasmic reticulum-retention motif in an intracellular loop of the kainate receptor subunit KA2. J Neurosci 26:7014-7021.
- Yamano Y, Takenouchi N, Li HC, Tomaru U, Yao K, Grant CW, Maric D, Jacobson S (2005) Virus-induced dysfunction of CD4+CD25+ T cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated neuroimmunological disease. J Clin Invest 115:1361-1368.
- Purow B, Haque RH, Noel MN, Su Q, Lee J, Burdick M, Lee J, Sundaresan T, Pastorino S, Park JK, Mikolaenko I, Maric D, Eberhart CG, Fine HA (2005) Expression of Notch-1 and its ligands, Delta-like-1 and Jagged-1, is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res 65:2353-2363.
- Lawrence DM, Durham LC, Schwartz L, Seth P, Maric D, Major EO (2004) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of human brain-derived progenitor cells. J Virol 78:7319-7328.
- Nadareishvili ZG, Li H, Wright V, Maric D, Warach S, Hallenbeck JM, Dambrosia J, Barker JL, Baird AE (2004) Elevated pro-inflammatory CD4+CD28- lymphocytes and stroke recurrence and death. Neurology 63:1446-1451.
- Cohen RI, Rottkamp DM, Maric D, Barker JL, Hudson LD (2003) A role for semaphorins and neuropilins in oligodendrocyte guidance. J Neurochem 85:1262-1278.
- Tomaru U, Yamano Y, Nagai M, Maric D, Kaumaya PT, Biddison W, Jacobson S (2003) Detection of virus-specific T cells and CD8+ T-cell epitopes by acquisition of peptide-HLA-GFP complexes: analysis of T-cell phenotype and function in chronic viral infections. Nature Medicine 9:469-476.